Chapter 5
Making Images from Interferometer Data
This chapter is devoted to the use of 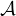
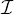
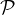
 to make and improve images from interferometer visibility
data. It begins with a brief description of the routes by which such data arrive in
to make and improve images from interferometer visibility
data. It begins with a brief description of the routes by which such data arrive in 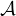
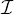
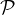
 . The basics
of weighting, gridding, and Fourier transforming the data to make the so-called “dirty” image are
described, followed by a discussion of deconvolution, particularly Clean. The output of Clean is a model
of the sky which, in cases of good signal-to-noise, can be fed back to improve the calibration of the
interferometer data, a process called “self-calibration.” How this is done in
. The basics
of weighting, gridding, and Fourier transforming the data to make the so-called “dirty” image are
described, followed by a discussion of deconvolution, particularly Clean. The output of Clean is a model
of the sky which, in cases of good signal-to-noise, can be fed back to improve the calibration of the
interferometer data, a process called “self-calibration.” How this is done in 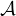
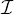
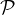
 is described. This entire
process often isolates bad data samples, not previously removed from the data set. An interactive,
baseline-based data editor called EDITR is described at the end of the chapter. You may find it more
useful than TVFLG (§O.1.6) for removing data at this stage in the processing. Task IMAGR now does
“3-dimensional” imaging, SCMAP contains an editing option at each self-calibration cycle, and EDITR has replaced
IBLED as the baseline-based editor of choice. A UV -plane based interactive editor called UFLAG is now
available.
is described. This entire
process often isolates bad data samples, not previously removed from the data set. An interactive,
baseline-based data editor called EDITR is described at the end of the chapter. You may find it more
useful than TVFLG (§O.1.6) for removing data at this stage in the processing. Task IMAGR now does
“3-dimensional” imaging, SCMAP contains an editing option at each self-calibration cycle, and EDITR has replaced
IBLED as the baseline-based editor of choice. A UV -plane based interactive editor called UFLAG is now
available.
Lists of 
 software appropriate to this chapter can be obtained at your terminal by typing ABOUT UV C R,
ABOUT CALIBRATION C R, ABOUT EDITING C R, and ABOUT IMAGING C R. Relatively recent versions of these lists are
also given in Chapter 13 below. Basic data calibration is discussed in Chapter 4, editing is discussed in §4.3.5 and
§8.1, and imaging and self-calibration are also discussed in §8.4 for spectral-line data and in §9.7 for VLBI
data.
software appropriate to this chapter can be obtained at your terminal by typing ABOUT UV C R,
ABOUT CALIBRATION C R, ABOUT EDITING C R, and ABOUT IMAGING C R. Relatively recent versions of these lists are
also given in Chapter 13 below. Basic data calibration is discussed in Chapter 4, editing is discussed in §4.3.5 and
§8.1, and imaging and self-calibration are also discussed in §8.4 for spectral-line data and in §9.7 for VLBI
data.
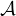
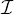
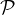
 to make and improve images from interferometer visibility
data. It begins with a brief description of the routes by which such data arrive in
to make and improve images from interferometer visibility
data. It begins with a brief description of the routes by which such data arrive in 
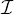
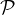
 . The basics
of weighting, gridding, and Fourier transforming the data to make the so-called “dirty” image are
described, followed by a discussion of deconvolution, particularly Clean. The output of Clean is a model
of the sky which, in cases of good signal-to-noise, can be fed back to improve the calibration of the
interferometer data, a process called “self-calibration.” How this is done in
. The basics
of weighting, gridding, and Fourier transforming the data to make the so-called “dirty” image are
described, followed by a discussion of deconvolution, particularly Clean. The output of Clean is a model
of the sky which, in cases of good signal-to-noise, can be fed back to improve the calibration of the
interferometer data, a process called “self-calibration.” How this is done in 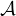
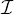
 is described. This entire
process often isolates bad data samples, not previously removed from the data set. An interactive,
baseline-based data editor called EDITR is described at the end of the chapter. You may find it more
useful than TVFLG (§O.1.6) for removing data at this stage in the processing. Task IMAGR now does
“3-dimensional” imaging, SCMAP contains an editing option at each self-calibration cycle, and EDITR has replaced
IBLED as the baseline-based editor of choice. A UV -plane based interactive editor called UFLAG is now
available.
is described. This entire
process often isolates bad data samples, not previously removed from the data set. An interactive,
baseline-based data editor called EDITR is described at the end of the chapter. You may find it more
useful than TVFLG (§O.1.6) for removing data at this stage in the processing. Task IMAGR now does
“3-dimensional” imaging, SCMAP contains an editing option at each self-calibration cycle, and EDITR has replaced
IBLED as the baseline-based editor of choice. A UV -plane based interactive editor called UFLAG is now
available.